Nutrition and a healthy growth track
Making sure that children get all the nutrients they need is not such an easy task. You might be wondering if your child is not growing well, is too skinny, needs to catch up on growth or even to gain weight. Oral nutritional supplements might be able to help in certain situations.
Keeping children on the right growth track can feel like a fulltime job for parents.
When should I worry about my child’s growth?
Certain signals start making us worry as parents. If you have any concerns about the following, talk to your doctor or healthcare professional.
Nutrition is essential to growth and Development
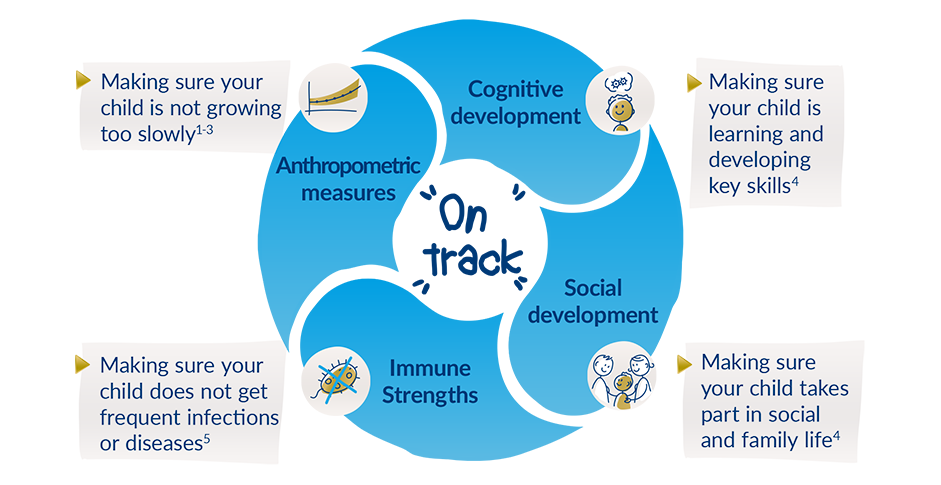
Nutrition and healthy growth & development go hand in hand. Your doctor or healthcare professional will look at a number of factors that reflect overall growth, including physical measurements (height, weight and waist circumference), intellectual & social development and immune strength.
If any of these areas seem to be going off track, your doctor may start by asking about your child’s nutrition to address any issues as quickly as possible.
Certain eating behaviours can jeopardise a child’s health
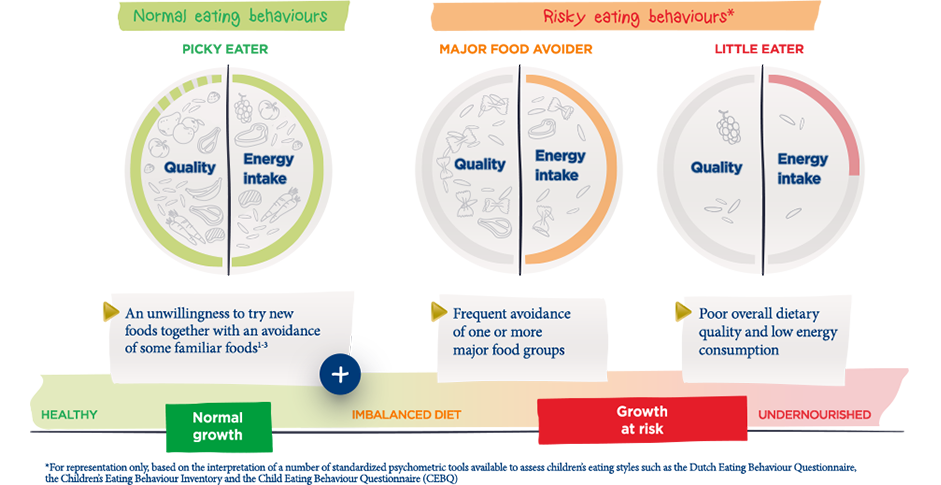
Having a rich and diverse diet helps to ensure that we get the nutrition our bodies need to maintain good health. Especially in children, good nutrition is essential to helping them reach their full growth potential. We have all experienced and seen the eating behaviours of children change over time. Some eating behaviours may put children at risk of not obtaining quality nutrients and the energy needed for growth and development6.
Picky eating alone is not a reason to worry. Children go through phases of not wanting to try new foods or showing very strong preferences. This does not have a negative long-term impact on health.
Risky eating behaviours can lead to nutritional deficiencies that may have major effects on a child’s development over time.
Childhood growth is a way to measure a child’s health and development. Keeping them on track can have a positive impact on their health and wellbeing throughout their lifetime.
Nutritional intervention is advised
When faced with the risk of nutritional deficiency, intervention is advised to support and maximize a child’s full potential. Take appropriate steps to help children get back on track. Re-establish a healthy diet when necessary, with an appropriate quantity and variety of nutrients.
Guidelines recommend solutions, such as oral nutritional supplements, to help children with or at risk of nutritional deficiencies7.
Oral nutritional supplements can help children catch up: improve body weight, growth and development8,9.

Nutren® Junior has been scientifically designed to help a child get back and stay on track to reach full potential with the B.I.G formula. You can learn more about Nutren® Junior, an oral nutritional supplement here.
References:
1. Ogata B, et al. Nutrition in childhood, in Krause's Food & the Nutrition Care Process, eds. Mahan LK and Raymond JL. Saunders, 14th Edition. 2016;Chapter 17:314-329. eBook ISBN:9780323340809.
2. Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Clinical Growth Charts. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/growthcharts/clinical_charts.htm. [last accessed 03/12/2019].
3. Ong KK. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol. 2017;31(5):463-464.
4. World Health Organization. Early child development. Available at: https://www.who.int/topics/early-child-development/en/. [last accessed 03/12/2019].
5. World Health Organization. Children: Reducing mortality. Available at: http://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/children-reducing-mortality. [last accessed 03/12/2019].
6. Taylor CM, et al. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2019;73(6):869-878.
7. Hill SM. Paediatrics and Child Health. 2017;27(8):378-382.
8. Medical Nutrition International Industry. Oral NutritionaI Supplements to Tackle Malnutrition. 2012. Available at:https://medicalnutritionindustry.com/files/user_upload/documents/ONS_2012/Dossier2012FINAL2012-09-04.pdf. [last accessed 03/12/2019].
9. ASPEN Board of Directors and the Clinical Guidelines Task Force. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2002;26(1 Suppl):1SA-138SA.